Why Uttar Pradesh Is Emerging as India’s Next Industrial Hub?
A Rising Startup & Innovation Ecosystem
Startups taking root: According to Invest UP (the state’s investment promotion agency), Uttar Pradesh now hosts nearly 9% of India’s startups, with around 130,000 startups recognized by January 2024—half of them from Tier‑2 and Tier‑3 cities like Kanpur and Agra.
Fintech flourish: Noida has become a major fintech hub, hosting over 239 fintech companies including Paytm, Rapipay, and others.
IT‑ITeS & GCC boom: With NASSCOM naming Lucknow and Kanpur as emerging hubs for IT and BPM, and the 2024 Global Capability Centres (GCC) policy, UP is attracting major tech and back‑office operations
Example: Digital lenders and AI startups are increasingly choosing Lucknow for its growing talent pool and, soon, the proposed “AI City.” Gautam Buddha Nagar (Noida) is also transforming into a global tech corridor.
Pro‑Business Policies & Incentives
- Industrial Investment & Employment Promotion Policy 2022: Targets a $1 trillion UP economy by 2029. Companies choosing UP get to pick from capital subsidy, SGST reimbursement, or PLI top-up incentives—applied to large, mega, super‑mega, and ultra‑mega investments.
- FDI & data‑centre policy: Since late-2023, UP has offered exemptions on land acquisition and stamp duty to overseas investors, coupled with a Data‑Center Policy (2021) encouraging greenfield investments till 2025.
- Sectoral pushes: Over 20 distinct policies span EV manufacturing, food processing, defence, logistics, greenhouse farming, and more.
- Incentive snapshot: A new manufacturing unit could get up to 35% subsidy (capped at ₹5 cr) on capital investment, a 100% waiver on stamp duty and mandi fees, and 25% freight subsidy on exports.
Infrastructure Overhaul & Connectivity
UP is rapidly building the backbone for business:
- Expressway network:
- Purvanchal Expressway (340 km, operational since Nov 2021) links Lucknow to Ghazipur, powering eastern UP’s economy.
- Bundelkhand Expressway (296 km, opened July 2022) connects Etawah to Chitrakoot, enhancing connectivity for agro and tourism industries.
- Ganga Expressway (1,047 km, under construction; ~84% done by June 2025) is expected to catalyze industrial corridors from Meerut to Prayagraj.
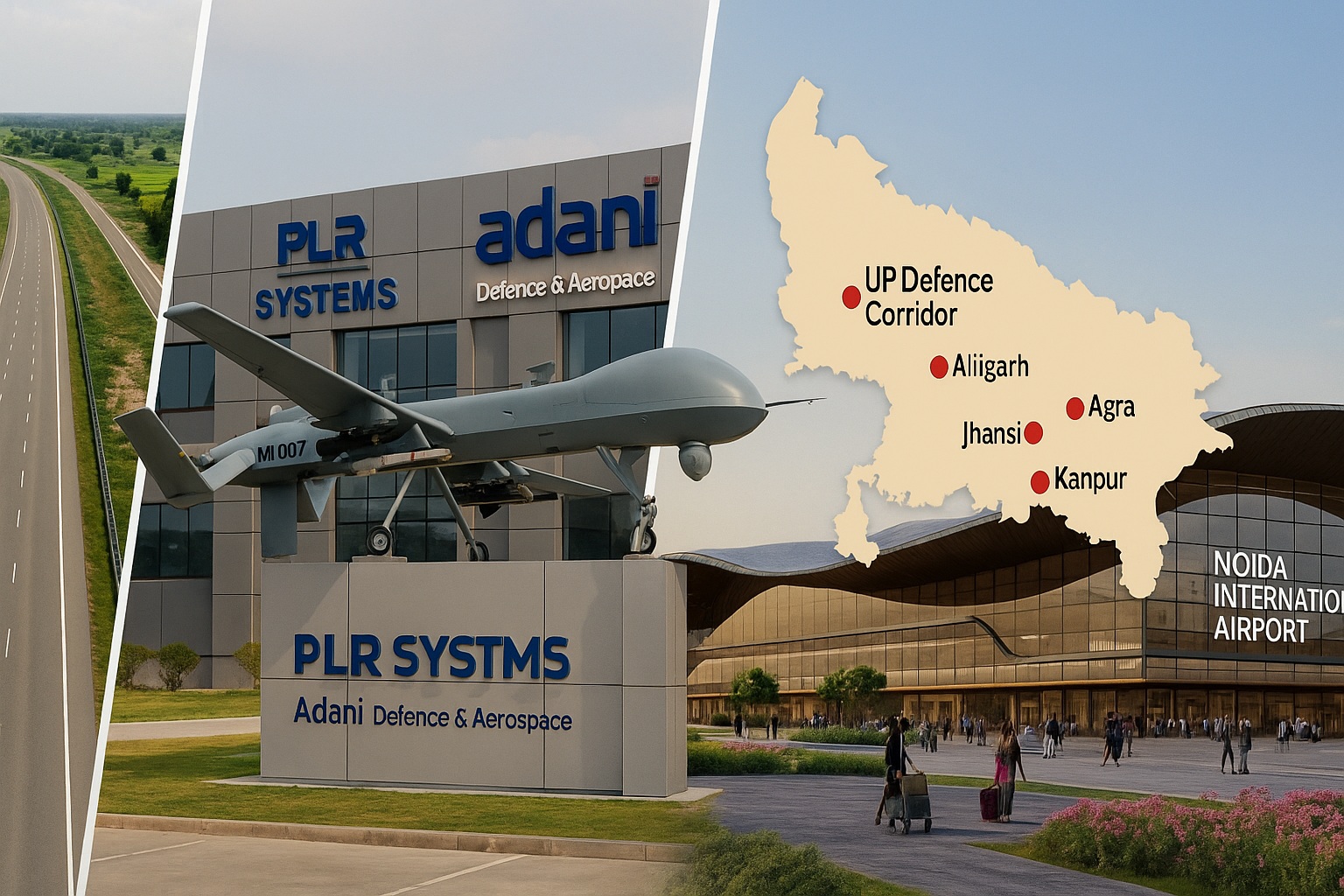
- Industrial cities & airports: YEIDA City (along Yamuna Expressway) is being planned as an integrated industrial-residential zone with its own Noida International Airport
Logistics Summit 2025: The government showcased doubling of per‑capita income in 7–8 years, and announced a new “Logistics Vision 2030.” India’s largest state-sponsored bulk drug/API plant is being set up in Lalitpur.
Key Sectoral Case Studies
Defence Manufacturing
UP Defence Industrial Corridor (UPDIC), spanning Aligarh, Agra, Jhansi, Kanpur, Lucknow, and Chitrakoot, has attracted 23 MoUs worth ₹50,000 crore since DefExpo 2020. Adani Defence & Aerospace committed ₹3,621 crore for ammunition/missile plants, generating ~4,000 jobs.
Agriculture & Food Processing
The state aims to increase horticulture area from 11.6% to 16% by 2027, and boost processing from 6% to 20%, backed by ₹11,000 crore investments and drip‑irrigation subsidies. As India’s top producer of mango, guava, cauliflower, and potato, UP is setting up Centres of Excellence and protected farming units to modernize agri-business.
Liquor & Excise Revenue
UP’s excise reforms, including lottery-based online liquor shop licensing, doubled state revenue from ₹23,927 crore (2018–19) to ~₹51,000 crore (2024–25), creating entrepreneurial opportunities and transparency.
MSMEs & Cottage Industries
The “One District One Product” initiative spans all 75 districts, supporting local artisans through training and branding. UP’s ODOP doubled exports since 2017; its products were even gifted during the G‑20 Summit.
Real‑Life Stories
- A rural artisan in Varanasi: Under ODOP, a brassware artisan saw his annual revenue triple after branding support and online marketplace integration—now exports his wares to Europe.
- Fintech in Noida: Rapipay set up operations in Noida, citing lower rentals and access to Delhi‑NCR talent—and benefitting from Invest UP’s ease of doing business portal.
- Farmers in Kanpur region: Joined drip irrigation subsidies, increasing yields by ~20% and selling through government‑facilitated mandis.
Ease of Doing Business & Government Push
- Digital facilitation: “Nivesh Mitra” portal and Invest UP streamline approvals, aim to reach $1 trillion state GDP by 2029.
- Power sector reforms: Though there are challenges—such as plans to privatize two power-distribution firms to reduce losses—UP’s leadership works with private investors to resolve bottlenecks.
Security & governance: Even the World Bank acknowledges UP’s strengthened law-and-order scenario, improved infrastructure, and strong MSME network (9.7 million units)
Challenges & the Road Ahead
- Power tariffs: Political voices argue rising tariffs could deter fresh investment.
- Execution risks: Some corridors like Bundelkhand Expressway faces structural issues.
- Sustainability of incentives: Long‑term competitiveness requires continued investment in human capital and resolving rural-urban divides.
Conclusion

Uttar Pradesh is transforming into India’s next major Industrial hub through a multifaceted strategy:
- Robust policy ecosystem: 20+ targeted sectoral incentives, streamlined approvals, and investor‑friendly regimes.
- World‑class infrastructure: Six expressways, planned industrial cities, and airport connectivity.
- Sectoral dynamism: Defence, fintech, agribusiness, data‑centres, liquor retail, and MSMEs.
- Startup culture: Nearly 9% of India’s startups, growth in GCCs and tech hubs.
- On‑ground impetus: Real stories of growth in rural artisans, fintech firms, and farmers.
If UP manages to maintain this momentum—addressing energy pricing and ensuring policy continuity—it is well-placed to surpass ₹1 trillion economy targets by 2029. In sum, the Yogi-Adityanath government has converted opportunity into action, making UP a belt of business growth that’s impossible for investors to ignore.
Top Government Schemes for Startups & MSMEs in Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh is fast becoming an Industrial hub for entrepreneurial energy in India. With lakhs of small businesses and startups emerging in both urban and rural areas, the state government and central government have launched several initiatives to support these ventures. Here’s a look at the top government schemes that are helping startups and MSMEs grow in Uttar Pradesh in 2025.
Udyam Registration – Gateway to Formal MSME Benefits
The Udyam Registration portal, launched by the Ministry of MSME, is a one-stop digital platform for classifying and availing benefits as a Micro, Small, or Medium Enterprise. In UP, over 25 lakh units have already registered, unlocking access to:
- Collateral-free loans under CGTMSE
- Subsidies under CLCSS (Credit Linked Capital Subsidy Scheme)
- Priority in government tenders
- Protection against delayed payments under MSME laws
Eligibility: Any business involved in manufacturing, trading, or services can register.
One District One Product (ODOP) – Local Pride, Global Reach

Uttar Pradesh’s ODOP scheme is a flagship initiative launched in 2018 and now expanded in 2025. Each of the 75 districts focuses on promoting one unique traditional product, such as:
- Bhadohi carpets
- Kannauj perfumes
- Moradabad brassware
- Barabanki handlooms
Through ODOP, artisans and MSMEs get:
- Skill development workshops
- Branding & packaging support
- Inclusion on e-marketplaces like GeM and ONDC
- Export promotion through UP Export Promotion Council
This initiative has helped double UP’s exports between 2017 and 2024, with MSMEs driving most of the growth and leading UP to become the next Industrial hub.
PMEGP – Turning Ideas into Income
The Prime Minister’s Employment Generation Programme (PMEGP) provides subsidized loans to individuals and groups for starting micro-enterprises.
- Loan Amount: Up to ₹25 lakh (manufacturing) / ₹10 lakh (services)
- Subsidy: 15–35% depending on category and area
- Who Can Apply: Anyone above 18 years, including new entrepreneurs
In UP, the Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC) and DICs actively promote this scheme. In 2023–24 alone, over 10,000 units were established, creating around 85,000 jobs in the state.
Yuva Udyami Yojana – Special Push for Young Entrepreneurs
Launched by the UP government, the Yuva Udyami Yojana provides low-interest loans and startup capital support for young entrepreneurs aged 18 to 40.
Key features:
- Loans up to ₹10 lakh – ₹25 lakh
- 50% interest subsidy for 2–3 years
- Priority for women, SC/ST, and rural youth
- Free mentorship via Incubation Centres
This scheme is integrated with Startup Nodal Agency UP and linked to incubation hubs at IIM Lucknow and IIT Kanpur.
Other Noteworthy Schemes
- Startup UP Policy (2020–25): Offers up to ₹50 lakh seed funding, co-working rental reimbursement, and patent filing assistance
- Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE): Zero collateral loans up to ₹2 crore
MUDRA Yojana: Loans up to ₹10 lakh for micro-entrepreneurs under Shishu, Kishore, and Tarun categories
Conclusion
With a growing ecosystem of policies, funding opportunities, and mentorship programs, Uttar Pradesh is supporting entrepreneurs like never before. Whether you’re a rural artisan, a college graduate with a startup idea, or a small manufacturer, 2025 is the right time to take advantage of these schemes and turn your dream into a sustainable business.
Tip: Always check the official websites (like msme.gov.in, kviconline.gov.in, and udyamregistration.gov.in) or visit your district industries center (DIC) for updated scheme details and application process.
Policy Lab: Analyzing the Success of ODOP in Uttar Pradesh
Introduction: The Vision Behind ODOP
Launched in 2018, the One District One Product (ODOP) scheme is a flagship initiative by the Government of Uttar Pradesh aimed at reviving and promoting traditional industries unique to each of the state’s 75 districts. The objective was simple yet powerful: “Local to Global” — to turn indigenous crafts into global brands and making Uttar Pradesh the next industrial hub.
Statistical Impact: Numbers That Tell the Story
The impact of ODOP over the past six years is clearly visible in data:
- Export growth: UP’s total exports increased from ₹88,000 crore (2017–18) to over ₹1.75 lakh crore in 2023–24, with ODOP products contributing nearly 30%.
- Employment boost: Over 25 lakh people—mainly rural artisans, weavers, and women—have found direct or indirect employment through ODOP-linked businesses.
- Skill development: More than 2 lakh artisans have been trained in design, quality control, and digital marketing under ODOP Skill Camps.
- GeM platform success: ODOP products from UP now feature prominently on the Government e-Marketplace (GeM) and ONDC, expanding access to buyers nationwide.
District Examples: Local Stories, Global Dreams
- Bhadohi (Carpets): Known as the ‘Carpet City of India’, Bhadohi exports woolen and cotton carpets worth ₹4,000+ crore annually.
- Kannauj (Perfumes): Ancient attars of Kannauj have found markets in UAE, France, and the US, with exports increasing 2.5x since 2020.
- Ambedkar Nagar (Textiles): Powerloom units have grown by 35%, thanks to upgraded machinery under the ODOP toolkit scheme.
Visual Transformation: Branding & Packaging
Before ODOP, many artisans packaged products in plain plastic or paper. Now, the scheme funds modern packaging, barcoding, labeling, and branding — making products shelf-ready for global markets. Product showcases at events like G20, Dubai Expo, and Pravasi Bharatiya Divas have significantly boosted visibility.
Expert Opinion: Why ODOP Works
“ODOP is not just a scheme; it’s a grassroots economic revolution. It strengthens rural economies, empowers women, and reduces migration,”
— Dr. Pankaj Kumar, Policy Analyst at IIFT.
“By combining culture with commerce, ODOP gives global exposure to India’s rich heritage,”
— Ritu Gupta, Director, Export Promotion Bureau, Uttar Pradesh.
Challenges Ahead
While ODOP has achieved much, issues like lack of credit access, digital literacy, and supply chain bottlenecks still need redressal. Many artisans require support in managing bulk orders, exports, and online marketing.
Conclusion: A Model Worth ScalingThe ODOP initiative has successfully turned Uttar Pradesh into a model of inclusive, craft-led economic growth. With the right push toward e-commerce, training, and export facilitation, ODOP could inspire similar models across India — and even globally.
Uttar Pradesh’s Economic Rise: A Case Study for Public Policy Students”
Introduction: India’s Most Populous State, now a Growth Engine
Uttar Pradesh (UP), long seen as a laggard in economic rankings, is now making headlines as one of India’s fastest-growing state economies. With a strategic push on infrastructure, governance reforms, and investor confidence, UP is emerging as a model for public policy transformation and being on the right track to become the next industrial hub.
GSDP Growth: From Stagnation to Momentum
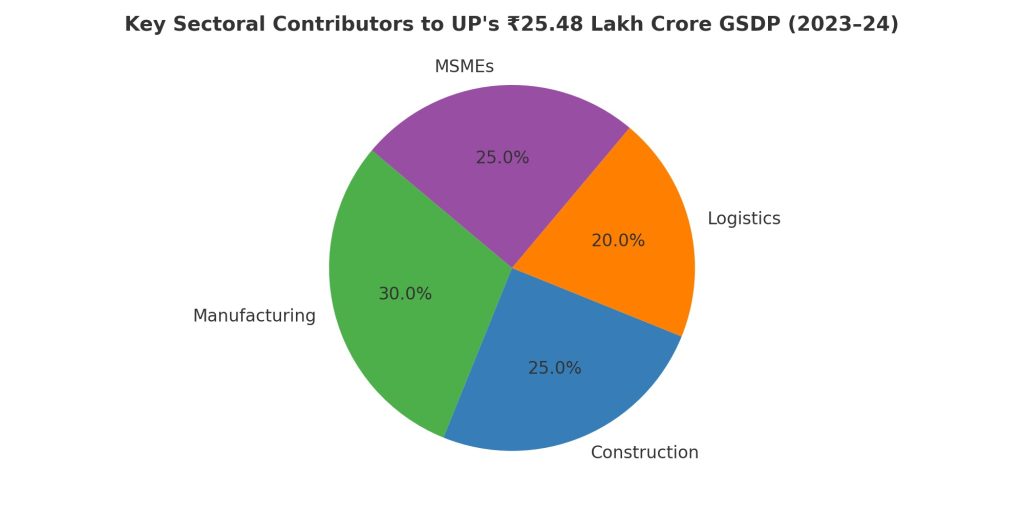
- UP’s Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) crossed ₹25.48 lakh crore in 2023–24, recording over 9% growth, placing it among the top five in India.
- The state’s ambition: become a $1 trillion economy by 2029, aligning with India’s $5 trillion vision.
This growth is driven by sectors like manufacturing, construction, logistics, and MSMEs, which collectively form the economic backbone.
Mega Infra Projects: The Development Blueprint
Infrastructure is at the heart of UP’s economic reboot:
- Expressways: Purvanchal, Bundelkhand, and Ganga Expressways are transforming regional connectivity.
- Noida International Airport: Set to be Asia’s largest upon completion, boosting aviation and logistics.
- UP Defence Corridor: Across six districts, encouraging Make in India in arms manufacturing.
Such projects are not just building roads—they’re unlocking economic corridors and witnessing the growth of Uttar Pradesh as the next industrial hub.
Investment Inflows: Building Investor Trust
- The UP Global Investors Summit 2023 attracted MoUs worth ₹36+ lakh crore, with sectors like renewable energy, defence, electronics, and data centres leading.
- District-level investment desks and the Nivesh Mitra single-window system have improved ease of doing business.
Result: UP is now among the top 3 states in attracting private investment.
Policy Reforms: A Pro-Business Governance Model
- Sector-specific policies: From EVs and MSMEs to warehousing and tourism, UP has over 20 focused industrial policies.
- Law and order: Improved safety and fast-track courts have boosted investor confidence.
- Labour reforms, land banks, and digital approvals have minimized bureaucratic hurdles.
Conclusion: A Living Policy Lab
UP’s transformation offers public policy students a real-world case of turning scale into strength. With effective planning, political will, and citizen-focused reform, even the most complex states can reposition themselves as economic powerhouses. With the combined efforts of the government, business and workers, the dream to see Uttar Pradesh as the next industrial hub is not too far.

